Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated auxin signaling inferred from the rice mutant osaxr.
Meng Y, Chen D, Ma X, Mao C, Cao J, Wu P, Chen M
Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Mar;5(3):252-4.
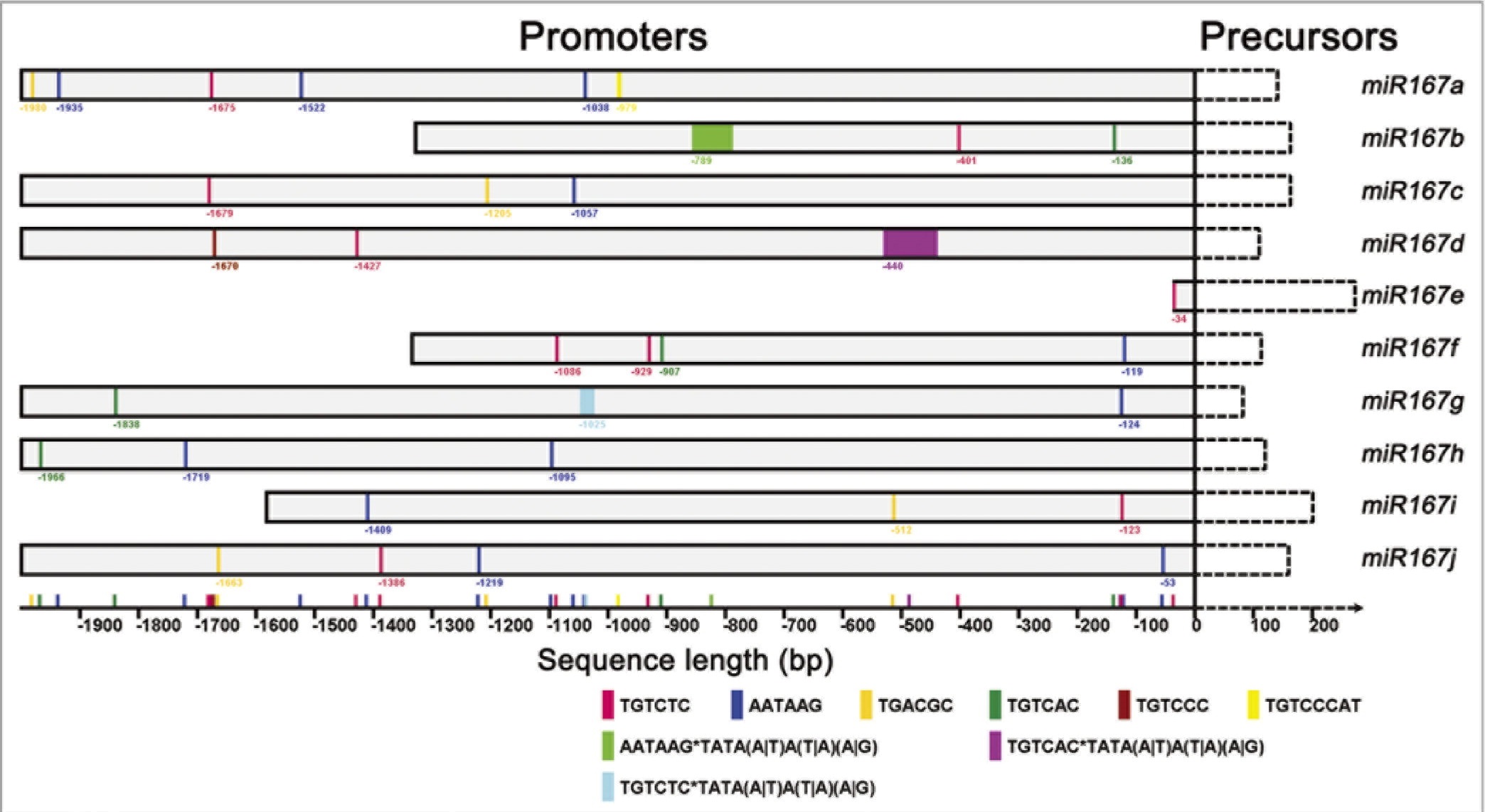
Auxin, known as the central hormone, plays essential roles in plant growth and development. In auxin signaling pathways, the tiny RNA molecules, i.e., microRNAs (miRNAs), show their strong potential in modulating the auxin signal transduction. Recently, we isolated a novel auxin resistant rice mutant osaxr (Oryza sativa auxin resistant) that exhibited plethoric root defects. Microarray experiments were carried out to investigate the expression patterns of both the miRNAs and the protein-coding genes in osaxr. A number of miRNAs showed reduced auxin sensitivity in osaxr compared with the wild type (WT), which may contribute to the auxin-resistant phenotype of the mutant. Auxin response elements (AuxREs) were demonstrated to be more frequently present in the promoters of auxin-related miRNAs. In our previous report, a comparative analysis of miRNA and protein-coding gene expression datasets uncovered a number of reciprocally expressed miRNA-target pairs. A feedback circuit between miRNA and auxin response factor (ARF) was then proposed. Here, we will discuss in-depth some points raised in the previous report, in particular, the organ-specific expression patterns of miR164, the feedback regulatory model between miR167 and certain ARFs, and the potential signal interactions between auxin and nutrition or stress that are mediated by miRNAs in rice roots.