Capture of regulatory factors via CRISPR-dCas9 for mechanistic analysis offine-tuned SERRATE expression in Arabidopsis.
Chen W, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhu T, Zheng Y, Hawar A, Chang Y, Wang X, Li D, Wang G, Yang W, Zhao Y, Chen D, Yuan YA, Sun B.
Nat Plants. 2024 Jan;10(1):86-99. doi: 10.1038/s41477-023-01575-x. Epub 2024 Jan2.
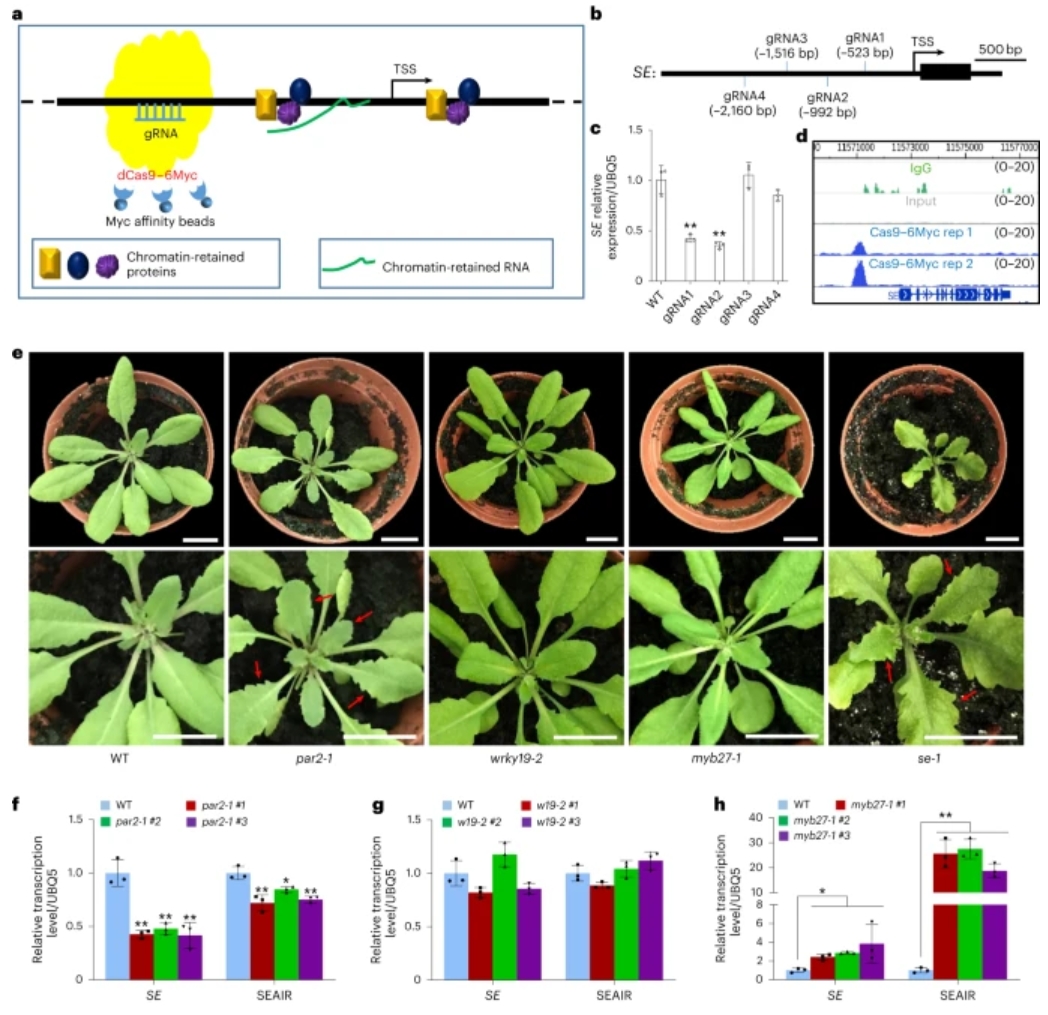
SERRATE (SE) plays an important role in many biological processes and underbiotic stress resistance. However, little about the control of SE has beenclarified. Here we present a method named native chromatin-associated proteomeaffinity by CRISPR-dCas9 (CASPA-dCas9) to holistically capture native regulatorsof the SE locus. Several key regulatory factors including PHYTOCHROME RAPIDLYREGULATED 2 (PAR2), WRKY DNA-binding protein 19 (WRKY19) and the MYB-familyprotein MYB27 of SE are identified. MYB27 recruits the long non-coding RNA-PRC2(SEAIR-PRC2) complex for H3K27me3 deposition on exon 1 of SE and subsequentlyrepresses SE expression, while PAR2-MYB27 interaction inhibits both the bindingof MYB27 on the SE promoter and the recruitment of SEAIR-PRC2 by MYB27. Theinteraction between PAR2 and MYB27 fine-tunes the SE expression level atdifferent developmental stages. In addition, PAR2 and WRKY19 synergisticallypromote SE expression for pathogen resistance. Collectively, our resultsdemonstrate an efficient method to capture key regulators of target genes anduncover the precise regulatory mechanism for SE.