Single-cell transcriptome analysis dissects lncRNA-associated gene networks in Arabidopsis.
He Z#, Lan Y#, Zhou X#, Yu B#, Zhu T, Yang F, Fu LY, Chao H,Wang J, Feng RX, Zuo, Lan W, Chen C, Chen M, Zhao X, Hu K, Chen D*
Plant Commun. 2023 Sep 14:100717. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100717.
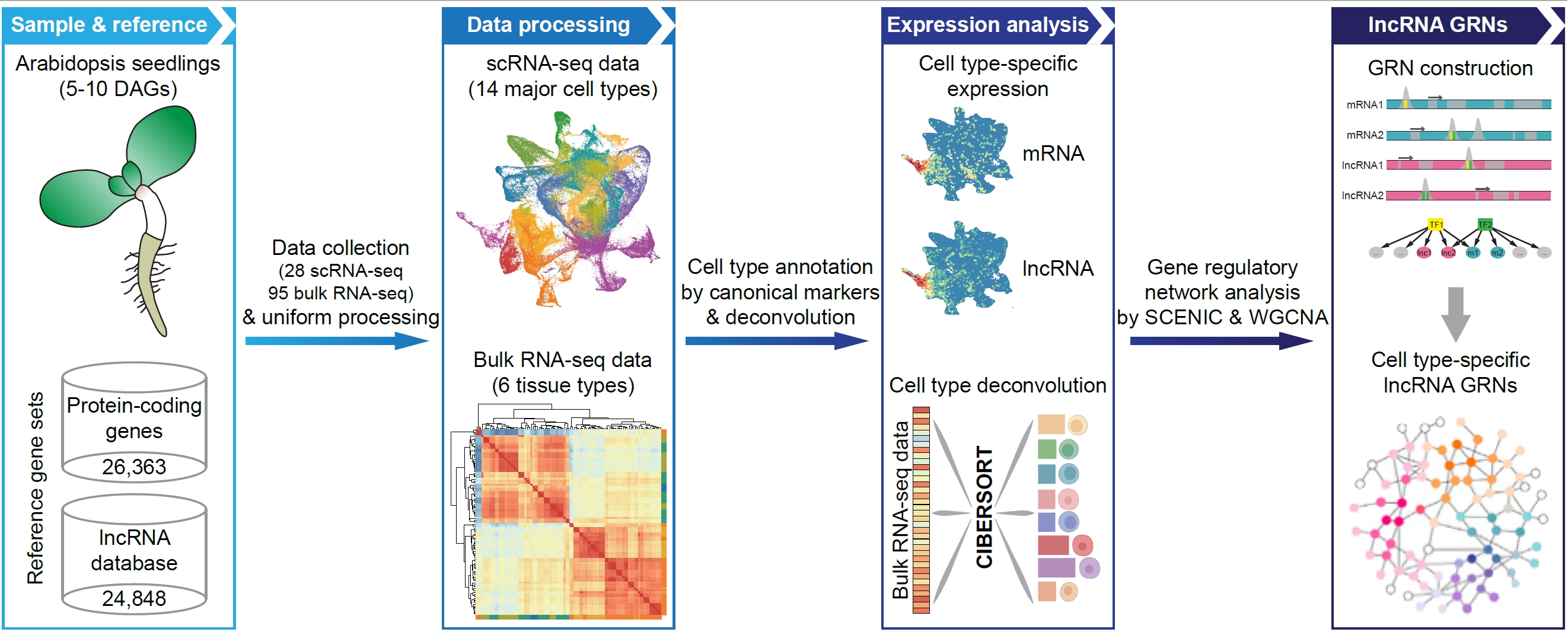
The plant genome produces an extremely large collection of long noncoding RNAs(lncRNAs) that are generally expressed in a context-specific manner and havepivotal s in regulation of diverse biological processes. Here we mapped thetranscriptional rogeneity of lncRNAs and their associated gene regulatorynetworks at single-cell retion. We generated a comprehensive cell atlas atthe whole-organism level by integra analysis of 28 published single-cellRNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets from Arabiis juvenile seedlings. We thenprovided an in-depth analysis of cell type-related ln signatures that showsconsistent expression patterns with canonical protein-coding markers. Wefurther demonstrated that the cell-type specific expression of lncRNAs elyexplains their tissue specificity. In addition, we predicted gene regulatorynetw based on motif enrichment and co-expression analysis of lncRNAs andmRNAs, and idened putative transcription factors orchestrating the celltype-specific lncRNA expres. The above analysis results are available at thesingle cell-based plant lncRNA atlatabase (scPLAD;https://biobigdata.nju.edu.cn/scPLAD/). Overall, this work demonstr thepower of integrative single-cell data analysis applied to plant lncRNA biologyarovides fundamental insights into lncRNA expression specificity andassociated gene lation.