Network biology bridges the gaps between quantitative genetics and multi-omicsto map complex diseases.
Wu S, Chen D, Snyder MP
Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Feb;66:102101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.102101.
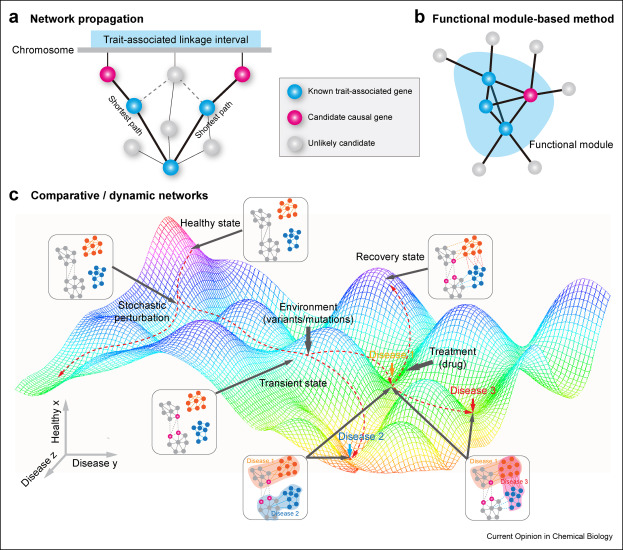
With advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies, quantitative geneticsapproac hes have provided insights into genetic basis of many complex diseases.Emerging in-depth multi-omics profiling technologies have created excitingopportunities for systematica lly investigating intricate interaction networkswith different layers of biological molecules underlying disease etiology.Herein, we summarized two main categories of biologi cal networks: evidence-basedand statistically inferred. These different types of molecular networkscomplement each other at both bulk and single-cell levels. We also review t hreemain strategies to incorporate quantitative genetics results with multi-omicsdata by network analysis: (a) network propagation, (b) functional module-basedmethods, (c) co mparative/dynamic networks. These strategies not only aid inelucidating molecular mechanisms of complex diseases but can guide the searchfor therapeutic targets.